This Waste Management Plan (WMP) sets out in
detail the approaches CRBC �V KADEN JV should adopt in the management of waste
generated from the various different construction activities. It also sets out the
procedures for the waste management activities and requirements during the
construction.
To demonstrate the
Project Team��s commitment on the continual improvement of our waste management
performance, the project waste management policy has been established as below:

The following
legislation relates to the handling, treatment and disposal of wastes in Hong
Kong, and should be observed with regard to all wastes generated and requiring
disposal due to the construction, where applicable:
�P
Waste Disposal Ordinance (Cap 354)
�P
Waste Disposal (Chemical Waste)
(General) Regulation (Cap 354)
�P
Waste Disposal (Charges for Disposal of
Construction Waste) Regulation (Cap 354)
�P
Land (Miscellaneous Provisions)
Ordinance (Cap 28)
�P
Public health and Municipal Services
Ordinance (Cap 132) �V Public Cleansing and Prevention of Nuisances (Urban
Council) and (Regional Council) By-Laws
The Waste Disposal
Ordinance (WDO) prohibits the unauthorized disposal of wastes. The illegal tipping or flytipping
of wastes on unauthorized sites is also controlled under the WDO. Under the
Waste Disposal (Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme) Regulation,
project team should apply for a billing account from EPD for disposal of
construction wastes generated from the project. The regulation prescribes the
requirements of handling of construction wastes on site and the construction
waste disposal-charging scheme.
Under the Waste
Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General) Regulation all producers of chemical wastes
(including asbestos) must register with EPD and treat their wastes either
utilizing on-site plant licensed by EPD, or arranging for a licensed collector
to take the wastes to a licensed facility. The regulation also prescribes the
storage facilities to be provided on site, including labeling warning signs,
and requires the preparation of written procedures and training to deal with
emergencies such as spillages, leakages or accidents arising from the storage
of chemical wastes.
Construction wastes that are wholly inert would be taken to public
dumps. Public dumps usually form part of land reclamation schemes operated by
the Civil Engineering and Development Department (CEDD). The Land
(Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance requires that individuals or companies who
deliver suitable construction wastes to public dumps obtain dumping licenses.
CEDD issues the licenses under delegated powers from the Director of Lands.
The Public Cleansing and Prevention of Nuisances By-Laws provide
further controls on the illegal tipping of wastes on unauthorized (unlicensed)
sites.
The project team should obtain all necessary permits and licenses under
these ordinances including, but not limited to:
�P
Chemical waste permits/ licenses under
the Waste Disposal Ordinance (Cap 354)
�P
Billing Account for construction waste
disposal-charging scheme (Cap 354)
The following
guidelines related to waste management and disposal would be adhered to during construction
of the project:
�P
Waste Disposal Plan for Hong Kong
(1989), Planning, Environmental and Lands Branch, Hong Kong Government
Secretarial
�P
Environmental Guidelines for Planning
in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Planning Standards and Guidelines (1990)
�P
New Disposal Arrangements for
Construction Waste. EPD and CED (1992)
�P
Code of Practice on the Packaging,
Labeling and Storage of Chemical Wastes (2002), Environmental Protection
Department
�P
Code of Practice on the Handling
Transportation and Disposal of Asbestos Waste, Environmental Protection
Department
�P
Code of Practice on the Handling,
Transportation and Disposal of Asbestos Waste
�P
Code of Practice for Demolition of
Buildings 2004
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
12/00, Fill Management
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
32/92, The Use of Tropical Hard Wood on Construction Site
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
2/93, Public Dumps
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
16/96, Wet Soil in Public Dumps
�P
Works Bureau Technical Circular No.
4/98, Use of Public Fill in Reclamation & Earth Filling Projects
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
5/98, On-site Sorting of Construction Waste on Demolition Site
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
29/00, Waste Management Plan
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
25/99, 25/99A and 25/99 Incorporation of Information on Construction and
Demolition Material Management in Public Works Sub-committee Papers
�P
Environmental, Transport and Works
Branch Technical Circular No. 33/02, Management of Construction and Demolition Material
Including Rocks
�P
Works Branch Technical Circular No.
6/02 and 6/02A, Enhanced Specification for Site Cleanliness and Tidiness
�P
Works Bureau Technical Circular No.
31/04 Trip Ticket System for Disposal of Construction & Demolition
Materials
�P
Works Bureau Technical Circular No.
15/03, Waste Management on Construction Sites
�P
Works Bureau Technical Circular No.
22/03, Additional Measures to Improve Site Cleanliness and Control Mosquito
Breeding on Construction Site
�P
Waste Reduction Framework Plan, 1998 to
2007, Planning, Environmental and Lands Bureau, Government Secretariat, 5
November 1998
�P
A Guide to the Registration of Chemical
Waste Producers
�P
A Guide to the Chemical Waste Control
Scheme
�P
Practice Notes for Authorized Persons
and Registered Structural Engineers (PNAP) 71
�P
Code of Practice: Safety and Health at
Work with Asbestos
�P
Code of Practice: Control of Asbestos
at Work
�P
Code of Practice for Demolition of
Building 2004
�P
Code of Practice on the Handling,
Transport and Disposal of Asbestos Waste
�P
Factories and Industrial Undertakings
(Asbestos) (Approval of Respiratory Protective Equipment) Notice
�P
Air Pollution Control Ordinance
�P
The Protection of Workers�� Health
Series �V Asbestos
�P
Construction Sites (Safety) Regulations
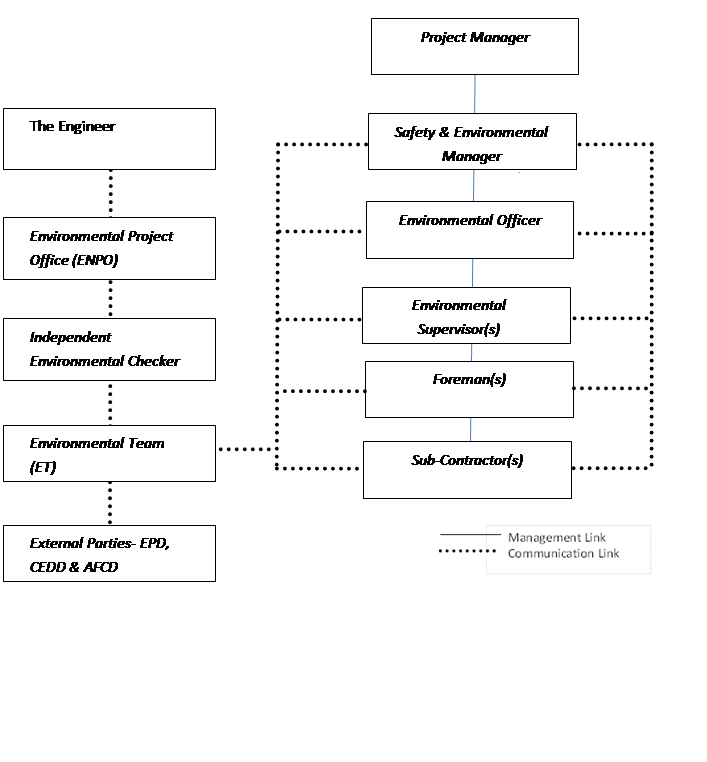
Appendix A of this WMP contains
a Project Organization Chart showing the reporting channels and functional
relationships of the various personnel currently employed and to be employed in
the future on this project.
All personnel of contractor team are required to implement waste management and
measures within their work area. A summary of the responsibilities of key
personnel:
The Engineer
The Engineer is responsible for overseeing
the construction works and for ensuring that the works are undertaken by the
Contractor in accordance with the specification and contractual requirements.
The duties and responsibilities of the Engineer with respect to EM&A may
include:
�P
Supervise the Contractor��s activities
and ensure that the requirements in relevant regulation and terms are fully
complied with.
�P
Inform the Contractor when action is
required to reduce environmental impacts in accordance with the Event and
Action Plans;
�P
Participate in joint site inspections
and audits; and
�P
Adhere to the procedures for carrying
out complaint investigations.
Environmental Project Office
The independent Environmental Project Office
(ENPO) is set up by the Client. The purpose of the ENPO is to oversee the
cumulative environmental impacts arising from this Contract and other
concurrent projects in the adjoining area and to liaise closely with the
mainland project teams for the HZMB Main Bridge.
Contractor
The Contractor (JV) shall:
�P
Ensure compliance with the procedures
and recommendations set out in this WMP;
�P
Work within the scope of the
construction contract and other tender documents;
�P
Participate in the site inspections
undertaken by the Environmental Team as required and undertake any corrective
actions instructed by the Engineer; and
�P
Take responsibility and strictly adhere
to the guidelines of the EM&A programme and
complementary protocols developed by their staffs.
The key personnel for environmental
matters include the Project Manager, Environmental Team Leader, Environmental
Officer and Environmental Supervisor.
Their responsibilities are listed below:
Project Manager
He is the Management Representative of the JV. His overall
responsibilities on environmental issues of the Project include:
�P Oversee the implementation of the WMP; and
�P Assign adequate resources for the implementation of the WMP.
Site Agent
His/ Her responsibilities include:
�P
Supervise & co-ordinate project
team and sub-contractors for construction works to meet the quality, safety
& environmental and schedule requirements
�P
Implement and adherence to statutory
environmental requirement
�P
Ensure design, work methods and
practices take due consideration of environmental requirements
�P
Release / accept work which complies
with contract / specification requirements
�P
Ensure that all project personnel are
adequately trained and experienced
�P
Ensure all necessary statutory permits
and license being applied
�P
Ensure all environmental mitigation
equipment and installations are well maintained
�P
Ensure the recommendations and
instruction from Engineer and Environmental Officer are implemented to improve
the environmental practice and carry out immediate action to rectify the
non-compliance of environmental requirements
�P
In the event of unwillingness of site
workers (including sub-contractors) to follow correct procedures, carry out
necessary actions to rectify the situation. Necessary actions include but not limited to administrative
charges, issue warning letter, expel from site and immediate termination of the
sub-contract.
�P
Carry out monthly environmental
management performance review with project team and review the overall
environmental performance on a quarterly basis. Report environmental
performance in Project Monthly Review Report
�P
Report any warning / advises received
from Government Authorities (e.g. EPD or Labour
Department)
�P
Maintain relevant environmental records
Environmental Team (ET) Leader
The leader of the Environmental Team shall be an independent party from
the Contractor and have relevant professional qualifications, or have
sufficient relevant EM&A experience subject to approval of the Engineer and
the EPD. The duties
of ETL are:
�P
Identify the
potential hazardous waste whenever possible and take proactive actions before
problems arise
�P
Provide
briefing to the contractor��s project team as necessary on the waste management
requirements.
Environmental Team (ET)
The ET Leader and the ET shall be employed to conduct the EM&A programme and ensure the Contractor��s compliance with the
project��s environmental performance requirements during the Contract. The
duties are:
�P
Environmental site surveillance;
�P
Audit of compliance with environmental
protection, and pollution prevention and control regulations;
�P
Monitor the implementation of
environmental mitigation measures;
�P
Monitor compliance with the
environmental protection clauses/specifications in the Contract;
�P
Adhere to the procedures for carrying
out complaint investigation, evaluation and identification of corrective
measures;
�P
Liaison with Independent Checker
(Environment) on all environmental performance matters, and timely submission
of all relevant EM&A preform for IEC��s approval;
�P
Advice to the Contractor on
environmental improvement, awareness, enhancement matters, etc., on site;
�P
Timely submission of the EM&A
report to the Project Proponent and the Director of Environmental Protection.
�P
Regularly
check the waste chit record to ensure the procedure observing the relative
environmental regulations.
�P
Ensure the
Contractor has implemented the mitigation measures as stated in the EM&A
Manual.
Environmental Officer
An Environmental
Officer will be present full time on site for inspection, supervision and
monitoring of the environmental performance, including waste management of the Contract. The duties of Environmental Officer in
the area of waste management will include:
�P
Assist the Q&E Manager in
preparation, implement and update the Waste Management Plan;
�P
Carry out inspections of the Site and
attend the weekly environmental walk for checking and identifying any waste
management practice on site not complying with this Plan and/ or relevant
environmental regulations in Hong Kong;
�P
Assist the Q&E Manager on the
implementation of site practice to meet the requirement on waste avoidance or
waste reduction;
�P
Advise the Q&E Manager on the
opportunities for reuse/ recycling of C&D materials generated on site;
�P
Properly keep the records of the waste
reuse, recycle or disposal for inspection by the Engineer;
�P
Maintain a database to trace the C&D
materials and waste to be generated from the project;
�P
Report and rectify any environmental
mal-practice on site to avoid the generation of unnecessary C&D materials
or waste from the project;
�P
Carry out training to the JV staff to
promote the environmental awareness.
Environmental Supervisor(s)
The Environmental Supervisor is an assistant to the EO in environmental
matters. He shall assist the EO in
his day-to-day management of on-site environmental issues and act on behalf of
the EO during his absence.
Site Engineer(s)/ Foreman(s)
The Site Engineers
/ Foremen appointed by the JV are responsible for the following duties in
relation to environmental control:
�P
Assist the project management team to implement
in the Contract all environmental related plans, including but not limit to
Environmental Management Plan, Waste Management Plan, Spoil Disposal Plan and
etc.;
�P
Control the Contract to fulfill the
requirement of waste management as detailed in this Plan;
�P
Ensure the disposal of C&D
materials and waste was directed to designated areas as approved by The
Engineer;
�P
Report to the Environmental Officer on
the non-compliance of the frontline operatives or the sub-contractors on
handling of the C&D materials and the waste as according to this Plan;
�P
Implement remedial actions or
mitigation measures on the non-compliance regarding the waste management on
site;
�P
Conduct environmental tool box talks to
the labourers and workers to make them aware of
environmental practice;
�P
Collaborate with the Environmental
Officer in the implementation of waste management measures;
�P
Assist the Environmental Officer in
arranging the necessary workforce for carrying out corrective actions.
Sub-contractor
All subcontractors
and other employees have the duty to carry out agreed waste management
practices as instructed by the Contract management. Every employee will report promptly to
project management any non-compliance of environmental protection and
mitigation measures. They will
actively participate in and co-operate with the Contract management to achieve
the environmental objectives.
Effective 2-way
communications will be developed to initiate the flow of environmental
information among different parties. The communication is mainly achieved
through the environmental correspondence, environmental report, SSEMC &
SSEC meeting, environmental briefing and training, site inspection, etc. and
environmental awareness promotion activities between the JV and site works and
sub-contractors.
Table 3.1 -
Means of Communications on Environmental Issues
|
Means
|
Frequency
|
Purpose/Action
|
Responsible Party
|
|
Environmental correspondence
|
As required
|
Written
communication among the ET, JV and the Engineer
|
ET, JV and Engineer Representative
|
|
Monthly Environmental report
|
Monthly
|
Report on
monitoring and audit results for the Project
|
EO
|
|
Notice of
exceedance, non-compliance, complaint
|
As required
|
Written notification
to different members of the JV requesting appropriate actions
|
JV, ET, Engineer Representative. Action according to procedures given in Sections 7.0.
|
|
licenses and
permits
|
As required
|
On receipt of a license
or permit, the original shall be kept at the site office and a copy shall be
sent to AECOM
|
EO
|
|
SSEMC & SSEC
meeting
|
Monthly
|
Face-to-face
communications between the ET and other disciplines
|
ET Leader, EO,
ES, Sub-contractors, Worker��s Representative
|
|
Weekly
Environmental Walk
|
Weekly
|
Face-to-face
communications between the EO and the ET Leader during the site inspection
|
EO, ES, Engineer
|
|
Induction
training
|
Contractual
requirement for new workers and sub-contractors
|
Promote awareness
of environmental procedures among workers and sub-contractors
|
EO, ES
|
|
Tool Box Talk
|
Contractual
requirement
|
Promote on-going
awareness of environmental procedures among workers and sub-contractors
|
EO, ES
|
|
Site inspection
|
Continually
|
Promote
awareness of environmental procedures among workers and sub-contractors via
routine and specific talks
|
ET Leader, EO,
ES
|
|
Environmental
records (i.e. Monthly Summary of WFT and Summary table on the use of timber)
|
Continually
|
Records of
training, permits, communications, etc., refer to Section 6
|
EO, to be kept
at site office
|
Note:
1. The follow-up actions on environmental issues in the SSEMC meetings and
SSEC meetings will be carried out ASAP and reported in the forthcoming meetings.
.The EO/ES shall monitor the progress of the follow-up actions.
2. The environmental records such as permits and licenses will be checked
by EO regularly to ensure that those records are valid and comply with the
ordinances.
Construction and Demolition (C&D) materials include public fill
(inert material) and C&D wastes (non-inert material). Public fill should
comprise broken concrete, brick and aggregates, etc. C&D wastes should
comprise unwanted materials generated during construction, including rejected
structures and materials, materials which have been over ordered or are surplus
to requirement and materials, which have been used and discarded.
The following
types of waste would be generated from the construction activities:
�P
Excavated material
�P
C&D material containing inert and non-inert materials
�P
Chemical waste
�P
General refuse
�P
Sewage
The disposal sites
for the wastes generated from the project as shown in the following table.
Table 4.1 -
Sources and Waste and Corresponding Disposal Site
|
Waste Type
|
Examples
|
Disposal Site
|
Estimate Volume
Generated
|
Estimate Volume Reused on/off-site
|
Estimate Volume Disposed off-site
|
|
Excavated material
|
�P
Rock
�P
Rubble
�P
Boulder
�P
Soil
�P
Sand
|
�P
Tuen Mun Area 38 Fill Bank�V for inert construction waste excluding slurry and bentonite;
�P
Tseung
Kwan O Area 137 Fill Bank �V for slurry and bentonite
|
452660 m3
|
112490 m3
|
340170 m3
|
|
C&D material �V public fill (inert)
|
�P
Broken concrete
�P
Brick
�P
Aggregate
�P
Asphalt
�P
Tile
�P
Masonry
�P
Used bentonite
|
3000 m3
|
1000 m3
|
2000 m3
|
|
C&D material �V C&D waste (non-inert)
|
�P
Wood
�P
Bamboo
�P
Plastic
|
�P
West New Territories (WENT) Landfill or other disposal outlets as
approved by the Engineer Representative
|
4800 m3
|
400 m3
|
4400 m3
|
|
Chemical waste
|
�P
Used oil
�P
Spent solvent
|
�P
Chemical Waste Treatment Facility at Tsing Yi
�P
Other approved facility
|
30 m3
|
N/A
|
30 m3
|
|
Chemical waste
(Asbestos)
|
�P
Asbestos Cement pipe
|
�P
Landfill or other disposal outlets as approved by the Engineer
|
0
|
N/A
|
0
|
|
General Refuse
|
�P
Packaging waste
�P
Office waste
|
�P
West New Territories (WENT) Landfill or other disposal outlets as
approved by the Engineer
|
2400 m3
|
N/A
|
2400 m3
|
|
Sewage
|
�P
Chemical toilet
�P
Site office toilet
|
�P
Licensed contractor
�P
Discharge to existing sewer
|
30 m3/d
20 m3/d
|
N/A
|
30 m3/d
20 m3/d
|
In order to make use of
C&D materials generated by the Site, JV will identify and use recycling
facilities or other construction sites where such materials can be used before
obtaining the written approval of the Engineer. Relevant information should be
submitted to the Engineer as following:
(a)
A detailed
description of the alternative disposal ground, including location, lot number
(where appropriate), location plan and photographs of the proposed alternative
disposal grounds showing the surrounding environment and land use;
(b)
where the
alternative disposal ground is a private construction site, a letter from each
of the relevant authorities, such as Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation
Department, Lands Department and Planning Department, to comment on suitability
of the site under their respective purview, and a letter from the Authorized
Person of the development to confirm:-
1)
The C&D
materials for use in the development is acceptable;
2)
The
land/pond filling in the proposed alternative disposal ground and the use of
land so formed by the C&D materials are in conformity with the statutory
town plan/lease condition; and
3)
The
Engineer��s staffs are allowed to enter the alternative ground to conduct
inspections where necessary.
(c)
where the
alternative disposal is a private recycling facility, it is on the recyclers��
list for C&D materials recognized by EPD, as well as a letter from the
operator to confirm the Engineer��s staff are allowed to enter the recycling
facility to conduct inspections where necessary;
(d)
where the
alternative disposal ground is a construction site of Government (other than a
government contract quarry), Hong Kong Housing Authority or Mass Transit
Railway Corporation, a written consent from the project office of the alternative
disposal ground to use the C&D materials generated from the Site;
(e)
where the
alternative disposal ground is a government contract quarry, a written consent
from the Mines Division of Civil Engineering and Development Department to
import the C&D materials generated from the Site;
(f)
the
estimated quantity and type of C&D materials to be used/processed in the
alternative disposal ground and the approximate delivery programme,
together with the name, post and specimen signature of the competent person to
sign the Disposal Delivery Form (DDF); and
(g)
a system for transmitting disposal records
from the alternative disposal ground to the Engineer��s Representative.
The purpose of this section is to describe the proposed mitigation
measures considered to ensure that all wastes generated during the construction
and demolition are well-managed on-site, transported and disposed of in a
manner that is both environmentally acceptable and in full compliance with
statutory and contractual requirements. A Site Layout Plan indicated the area
for the waste management such as temporary storage area, waste sorting area and
disposal area as presented in Appendix B.
�� Design and programme excavation works so that
the materials excavated can be re-used as back-fill material to balance cut and
fill and hence reduce the generation of excavated materials.
�� Right amount of raw materials should be ordered at the right time with
proper control and documentation on material flow to minimize over-ordering.
Raw materials should be fully utilized to avoid wastage
�� Surplus materials should be returned to stock in centralized area with
suitable protective measures. If possible, surplus materials should be exchange
with other sites, to minimize material wastage
�� Careful design and planning and good site management should be
maintained to minimize over ordering and generation of waste materials such as
concrete, mortars and cement grouts
�� Sequence of
demolition should be planned to allow the separation and sorting of building
materials.
�� Avoid, reduce or minimize the use of timber in temporary works
construction as far
�� as possible. Procedures of using timber should be established guiding the
use of timber on site, in order to reduce or minimize the use of timber. The
design of formwork should maximize the use of standard wooden panels so that
high level of reuse can be achieved
�� Steel false work should be used as much as possible to reduce the
amount of waste timber generated from the project
�� Current operation procedures including any waste reduction measures
should be reviewed, especially during installation and cutting, to avoid
unnecessary use
�� Broken items or offcuts should be used when sections of small lengths
are required
�� If cut and fill could not be balanced on-site, suitable excavated
materials should be sorted on site to recover the inert portions (e.g. soil and
broken rock) for reuse on site before the remaining materials are disposed off site or disposal to designated Public Filling Facility
�� Carefully plan/program excavation and backfilling activities so that
excavated materials can be used for backfilling within the site
�� Excavated material should be reused as close to the point of excavation
and as soon after excavation as possible and directly transferred to the area
of deposition, if practicable.
�� The inert C&D materials generated from the toll plaza cut slopes will be used for construction of the raised platform for the toll plaza where
possible.
�� All C&D materials arising from or in connection with demolition
work should be sorted on-site and be separated into different groups for
disposal at landfills, public filling facilities or recycling appropriate
�� Identify and list out all work processes or activities that should
generate reusable/ recyclable materials during construction and demolition
�� For those suitable inert C&D materials (e.g. broken concrete from
demolition or road improvement works) should be properly sorted for recycling
into aggregates and recover the materials for on -site usage
�� Demolition debris from demolition works should be sorted to recover on
site broken concrete, reinforcement bars, mechanical and electrical fittings as
well as other building services fittings / materials that have established
recycling outlets
�� Procedures of the handling of reusable/ recyclable materials should be
established
�� Recycle suitable C&D materials by transporting the materials to
designated C&D materials recycling facilities for processing
�� All materials should be reused on site as far as practicable, including
formwork plywood, hoardings, scaffolding, trench supports, topsoil and
excavated materials.
�� Where necessary, alternatives such as metal scaffolding, steel formwork
or plastic facing should be considered to increase the potential for reuse.
�� Suitable materials, such as metal should be recovered on site for
collection by recycling contractors
�� All cardboard and paper packaging (for plant, equipment and materials)
should be recovered on site, properly stockpiled in dry condition and covered
to prevent cross contamination by other C&D materials
�� Reputable recycling contractors with valid licenses and fulfilling all
the legislative requirements should be employed to facilitate that recyclable
materials sorted from the site are collected with reasonable care
�� The quantities of all the recyclable materials should be recorded
before removal off site
The materials stockpiled on-site should
be managed in order to prevent any potential impacts. Following measures should
be considered in order to properly manage the stockpiled materials:
�� Identify and
provide sufficient space for temporary storage of C&D materials to
facilitate collection and/ or sorting on site
�� Stockpiled
materials should be sited away from any stream courses so as to avoid releasing
materials into the water bodies
�� Demolished debris
should not be accumulated on the floors unless the debris accumulation is
justified by engineering calculations
�� No stockpile of
construction materials, debris, formworks, or other forms of obstructions is
allowed to block the accesses throughout the entire construction period
�� Location to
minimize visual impacts and nuisance related to noise and air quality (dust) to
any sensitive receivers
�� Storage of
material on site should be kept to a minimum to avoid nuisance to local
residents
�� Keeping the movement
of stockpiled material to a minimum
��
�� Stockpiled
materials should be covered by tarpaulins and/or watered as appropriate to
prevent windblown dust and/or surface run-off.
�� Measures such as
providing sand bag barriers should be provided to prevent the washing away of
construction materials, soil, silt or debris into any drainage system. Any
washout of construction or excavated materials should be diverted to the
drainage system via sediment traps
�� All surplus
excavated material generated from the project should be disposed of at the
designated Public Filling Facility
�� According to the
Waste Disposal (Charges for Disposal of Construction Waste) Regulation (Cap.
354N), Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme mentioned in Section 5.10 in
this WMP should be implemented during the construction.
�� The acceptance
criteria for Public Filling Facility and Landfill should be followed
�� All inert C&D
materials generated from this contract should be disposed of at the designated Public
Filling Facility. Such materials should be free from marine mud, household
refuse, plastic, metal, industrial and chemical waste, animal and vegetable
matter and other matter considered unsuitable by Filling Supervisor
�� All dump trucks
used for delivery of public fill to public filling facilities should have valid
Dumping Licenses issued by CEDD. The inert C&D materials delivered to the
public filling facilities should be in accordance with the conditions in the
dumping license
�� All non-inert
portions of C&D material (C&D waste) generated from the project should
be disposed of at the designated landfill and/ or other disposal outlet as
directed by the Engineer. Should provide EPD with one week��s advance notice
before starting to deliver the C&D waste to the landfills and should inform
EPD of any subsequent changes to the disposal programme
during the contract period
�� Trees and
vegetation should be stripped prior to site clearance, chopped and compacted
using suitable mobile compactors to reduce the volume of material to be
transported and disposed of
�� Should not permit
any sewage, wastewater or effluent containing sand, cement, silt or any other
suspended or dissolved material to flow from the site onto any adjoining land
or allow any waste matter or refuse which is not part of the final product from
waste processing plants to be deposited anywhere within the site or onto any
adjoining land
�� In order to
minimize the impacts of demolition works, the wastes should be cleared as
quickly as possible after demolition
�� When any
components of a structure or water mains to be demolished and are suspected to
be consisting of asbestos, the project team should inform the ER. Any work which involves the use or handling of asbestos containing
materials must strictly follow the following procedure:
�� employ a
registered asbestos consultant to conduct an asbestos investigation and prepare
an asbestos investigation report and an asbestos abatement plan;
��
�� submit the
asbestos investigation report and the asbestos abatement plan to the
Environmental Protection Department at least 28 days before start work on the
asbestos containing materials;
��
�� notify the
Environmental Protection Department of the date of commencement of work on
asbestos containing materials at least 28 days in advance;
��
�� employ a
registered asbestos contractor to carry out the asbestos work in accordance
with the asbestos abatement plan;
��
�� employ a
registered asbestos consultant to supervise the implementation of the asbestos abatement
plan and the work of the registered asbestos contractor; and
�� employ a registered asbestos laboratory to conduct sampling and analysis for
the asbestos work.
�� Responsible for
good site practices, arrangements for collection and effective disposal to an
appropriate facility, of all wastes generated at the site
�� Training of site
personnel in proper waste management and chemical waste handling procedures
�� Provision of
sufficient waste disposal points and regular collection for disposal
�� Appropriate
measures to minimize windblown litter and dust during transportation of waste
by either covering trucks or by transporting wastes in enclosed containers
�� Regular cleaning
and maintenance programme for drainage systems, sumps
and oil interceptors
�� A recording system
for the amount of wastes generated, recycled and disposed of (including the
disposal sites).
A trip ticket system (TTS) for the removal of
construction and demolition (C&D) materials from the Site to the designated
disposal ground or alternative disposal ground will be implemented as according
to the Particular Specification.
The system will be developed and presented in the Waste Management Plan
to be prepared for the project.
JV willl inform the
Engineer of the account number of the billing account for disposal of
construction waste under the Waste Disposal (Designated Waste Disposal
Facility) Regulation (Cap. 354L). This is to enable the Engineer to check the
disposal records posted at the Environmental Protection Department��s website.
The Engineer will provide the account number to the Civil Engineering and
Development Department for overall monitoring of the trip ticket system,
detecting and taking action to deal with malpractice such as overloading of
dump trucks and improper covering of load, and compiling statistics as well as
counting eligible trips for mechanical dump truck covers under the pay for
safety and environment scheme / pay for safety scheme.
Site Management
Plan for Trip Ticket Implementation
A Site Management Plan (The Plan) will be prepared which includes the
implementation of TTS. The Plan should include site organization and staff
duties, disposal programme, site procedures for duly completed of CHIT/DDF, as
presented in Appendix E and Appendix F etc.
A comprehensive register of the disposal delivery for recording the
disposal of C&D materials and waste will be established. The register will
also cover the recyclable materials removed by the recycling contractors off
the Site. The quantity (ton) of the C&D material shall be recorded in the
register.
Record Keeping
For the management of CHIT/DDF, the following procedures and record keep
will be implemented to all dumping activities.
(a) For each truckload of C&D materials leaving
the Site, the truck driver must bear a duly completed CHIT/ DDF;
(b) A daily record of disposal, as presented in Appendix D, of C&D materials from
the Site including CHIT/ DDF numbers, vehicle registration marks, drivers��
particulars, approximate volume, C&D materials type, designated disposal
ground, departure time from the Site, actual disposal ground and arrival time
at disposal ground should be maintained. Part 1of the DRS completed by JV in
duplicate and inform the Engineer��s staff before departure of the vehicle. The
Engineer��s staff shall sign Part 1 of the DRS before departure of the trucks,
or to suit site operations at other time to be agreed between the Engineer��s
Representative and JV;
(c) The truck shall proceed to the disposal ground
as stipulated in the designated disposal ground. The truck driver shall present
the CHIT/ DDF to the operator of the disposal ground. For a prescribed
facility, if the C&D materials accord with the acceptance criteria, disposal
of the materials will be permitted and the facility operator will give the
driver a Transaction Record Slip and stamp the CHIT.
(d)
For
disposal ground other than prescribed facilities, the DDF should be signed off
by a competent person as agreed by the Engineer at the disposal ground to
confirm completion of each trip. A daily record with details of each disposal
trip from the Site to the disposal ground will be maintained. The completed
Part 2 of the DRS form should be submitted to the Engineer.
Chemical waste, as defined under the Waste
Disposal (Chemical Waste) (General) Regulation, includes any substance being
scrap material, or unwanted substances specified under Schedule 1 of the Regulation.
Substances likely to be generated by construction activities arise from the
maintenance of construction plant and equipment. These include, but not limited
to the following:
��
Scrap batteries or spent acid/alkali from their maintenance;
��
Used engine oils, hydraulic fluids and waste fuel;
��
Spent mineral oils/cleaning fluids from mechanical machinery; and
��
Spent solvents/solution, some of which may be halogenated, from
equipment cleaning activities.
It is anticipated that the quantity of chemical
waste, such as lubricating oil and solvent produced from plant maintenance,
should be small for this project.
Storage, handling, transport and disposal of chemical waste should be
arranged in accordance with the Code of Practice on the Packaging, Labeling and
Storage of Chemical Waste published by EPD.
General:
�� No maintenance
activities which may generate chemical wastes should be undertaken directly on
the ground;
�� Stored volume shall not be kept more than 450 litres
unless the specification has been approved by the EPD. Storage area should be
enclosed by three sides by a wall, partition of fence that is at least 2m
height or height of tallest container with adequate ventilation and space;
�� Any unused chemicals or those with remaining functional capacity shall
be recycled;
Containers used for the storage of chemical wastes:
�� Be suitable for the substance they are holding, resistant to corrosion,
maintained in a good condition, and securely closed
�� Have a capacity of less than 450 litre unless
the specifications have been approved by EPD
�� Display a label in English and Chinese in accordance with instructions
prescribed in Schedule 2 of the Regulation
Labeling:
��
Every container of chemical waste
should bear an appropriate label containing the particular details of the
chemical waste it contained. The waste producer should ensure that the
information contained on the label is accurate and sufficient so as to enable
proper and safe handling, storage and transport of the chemical waste
Storage area:
��
Be clearly labeled and used solely for
the storage of chemical waste
��
Be enclosed on at least 3 sides
��
Have an impermeable floor and bounding of
sufficient capacity to accommodate 110% of the volume of the largest container
or 20% of the total volume of waste stored in that area, whichever is the
greatest
��
Have adequate ventilation
��
Be covered to prevent rainfall entering
��
Be arranged so that incompatible
materials are adequately separated
Disposal:
�� Be via a licensed waste collector
�� To a licensed disposal facility, such as Chemical Waste Treatment
Centre
Spillage:
��
Contact immediately
the Contracts Manager and/or Foreman and report the spillage
��
Establish source of
spill or discharge and determine nature of material
��
Where possible halt
discharge
��
Commencing at the
source of the spill, establish all current and potential impacted areas
following the flow/drainage/infiltration paths to limit of spill and project
future path
��
Establish priority
order for containment of spill based on assessment above
��
Commence containment
of spill using bunds made from available materials and ground water cut-off
trenches where necessary
��
After spill is
contained remove material (including contaminated soil where necessary) using
pumps and/or absorbent materials
��
Dispose of the materials, including the
contaminated soil as chemical waste
The presence of a construction site with large
numbers of workers and site offices should result in general refuse requiring
disposal. This should mainly consist of food waste, aluminium cans and waste
paper.
��
Temporary storage
areas should be identify and provided for the temporary storage of general
refuse to facilitate collection
��
General refuse
generated on-site should be stored in enclosed bins or compaction units
separate from construction and chemical wastes
��
Temporary storage
areas for general refuse should be enclosed to avoid environmental
impacts. Sufficient dustbins should
be provided for storage of waste as required under the Public Cleansing and
Prevention of Nuisances Ordinance (Regional Council) By-laws
��
General refuse
should be cleared daily and should be disposed of to the nearest licensed
landfill or refuse transfer station
��
Separate labelled
bins should be provided to segregate the waste generated by workforce. Waste
recycle collector should be employed to collect the segregated waste
��
Cardboard and paper
packaging (for plant, equipment and materials) should be recovered on site,
properly stockpiled in dry condition and covered to prevent cross contamination
by other C&D materials
��
Office waste should
be minimized through using papers on both sides. Communication by electronic
means should be used as far as possible
��
Open burning of
refuse on-site is prohibited by law and should not be undertaken
��
Toilet wastewater
should be transported by a licensed contractor to a Government Sewage Treatment
Works for disposal in accordance with the Sanitation and Conservancy (Regional
Council) By-laws
��
In temporary stage, sewer from toilet and domestic wastewater from other
source like hand and cup washing should be discharged into holding tank and collect by license
collector. Application of ��Discharging Waste
Water into Existing Sewage Manhole�� was submitted to DSD for approval.
In permanent stage,
sewer and domestic wastewater will be discharged to existing sewer,
subject to DSD approval. Estimated volume of sewage flow was shown in Table
4.1.
��
Wastewater from the
chemical toilet should be emptied by licensed collector regularly.
To maintain the site in a clean and tidy
condition during the construction, the following general measures should be
implemented on site at all times. Regular site inspections should be undertaken
by the site team to ensure that the following general measures are observed on
site:
Daily cleaning
should be performed daily after work within the site and the public areas
immediately next to the site. It covers:
��
Clear passageways, common accesses and public areas, keep them free
from obstruction
��
All access routes, including public access, staff access, loading/
unloading access of vehicles, emergency access and emergency vehicular access
should be kept tidy, safe and convenient
��
Storing and stacking materials properly. Clearing stockpile and wastes
��
Sorting, storage and/or disposal of waste materials in accordance with
the WMP
��
Securing hoarding, barriers, guarding, lighting, and signing of works
properly
��
Removal and prevention of any water ponds and
flooding
Weekly tidying should be performed weekly within the site as well as
the public areas immediately next to the site. It covers:
��
Thorough cleaning of passageways, common accesses and public areas
��
Re-organize storage of materials for better utilization of storage
spaces and safe stacking
��
Maintenance, re-conditioning and cleaning of plants, tools and
equipment
��
Collect and remove waste off site in accordance with the Waste
Management Plan
��
Clean, re-condition and/or replace the hoarding, barriers, guarding,
lighting and signage of works to good working condition
��
Clear drains and channels to prevent flooding
To control the rodent problem, the Site shall
be maintained in a tidy state at all times to discourage rodent harbourage and detect rodents at an early stage. Refuse and
food must be kept in containers with well-fitted covers/rodent proof store
rooms to deprive rodents of food. The Contractor shall not attempt to disinfect
rodents by themselves but shall appoint a pest control services contractor for
rodent control services or contact district pest control offices or the Pest
Control Advisory Section of the Food and Environmental Hygiene Department for
rodent control advice.
In order to enhance the awareness of the workers
including those of the sub-contractors�� on waste management on site,
site-specific induction training and regular toolbox talks topic related but
not limited to site cleanliness and appropriate waste management procedures
including waste reduction, reuse and recycling should be provided to all site
staff.
Environmental Officer should identify the need
and arrange relative trainings for all employee and the sub-contractors��
workers involved in the works.
The training should cover the waste management
policy, targets, measures for on-site sorting of C&D materials and
measurement on waste management performance on the site.
An auditable record should be maintained for all
environmental training undertaken.
Site environmental inspection should be conducted in a monthly basis.
The Environmental Officer or Site Administrator and the Engineer or his
delegate should attend the inspection, in order to evaluate the overall performance of the implementation of
the WMP and ensure the appropriate control measures are properly implemented. The inspection
should also cover waste sorting, storage and disposal.
The aims and objectives of waste management
inspection are:
�� To ensure that the waste arising from works are handled, stored,
collected, transported and disposed of in an environmentally acceptable manner;
�� To ensure that the handling, storage, collection and disposal of waste arising
from the works comply with the relevant requirements under the Waste Disposal
Ordinance and its regulations;
�� To encourage the reuse and recycling of materials.
Project team should
take immediate action to rectify the deficiencies identified from the
inspection and report the status of rectification actions in the Monthly
Environmental Report.
Table 11.1 - Event Action Plan
for Non-compliance
|
Step
|
Day
|
Action
|
Contractor
|
ER
|
|
1
|
1
|
Create a new non-compliance record within 1 working day after making
an observation during a site audit. The project team should send a Notice of
Non-Compliance (NNC) to the ER. The NNC should include the observations and
the reasons for non-compliance.
|
*
|
|
|
2
|
2
|
Propose
corrective actions within 1 working day after the issue of the NNC.
|
*
|
+
|
|
3
|
2
|
Review and
agree the proposed corrective actions and make additional recommendations as
required.
|
|
*
+
|
|
4
|
2
|
Implement the
proposed corrective actions once they have been agreed.
|
*
|
|
|
5
|
-
|
Check the
implementation of the corrective actions at the next site audit. Close the
non-compliance record if the implementation of the corrective actions is
satisfactory.
|
*
+
|
|
|
6
|
-
|
Propose
preventive actions within 3 working days after the closure of the
non-compliance record.
|
*
|
+
|
Note:
* Action
party
+ Comments
on the non-compliance record where applicable
ER Engineer��s
Representative
The EO shall check whether GCL
has followed the relevant contract specifications and the procedures specified
under the laws of Hong Kong. In addition to the site inspections, the ET shall
review the documentation procedures prepared by the GCL once a week to ensure
proper records are being maintained and procedures undertaken in accordance
with the Waste Management Plan. The checklist is given in below Table 11.2:
Table 11.2 �V Waste Management
Checklist
|
Activities
|
Timing
|
Monitoring Frequency
|
If non-compliance, Action Required
|
|
All necessary waste disposal permits
or licenses have been obtained
|
Before the commencement of demolition works
|
Once
|
Apply for the necessary permits/licences prior to disposal of the waste. The ET
shall ensure that corrective action has been taken.
|
|
Only licensed waste haulier are used for waste collection.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to use a licensed waste haulier.
The Contractor shall temporarily suspend waste collection of that particular
waste until a licensed waste haulier is used. Corrective action shall be undertaken
within 48 hours.
|
|
Records of quantities of wastes generated,
recycled and disposed are properly kept. For demolition material/waste, the
number of loads for each day shall be recorded (quantity of waste can then be
estimated based on average truck load. Should landfill charging be
implemented, the receipts of the charge could be used for estimating the quantity).
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
The Contractor shall estimate the missing data
based on previous records and the activities carried out. The ET shall audit
the results and forward to the ER and IEC for approval.
|
|
Wastes are removed from site in a timely
manner. General refuse is collected on a daily basis.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to remove waste accordingly.
|
|
Waste storage areas are properly cleaned
and do not cause windblown litter and dust nuisance.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to clean the storage area and/or cover the waste.
|
|
Different types of waste are segregated
in different containers or skip to enhance recycling of material and proper
disposal of waste.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to provide separate skips/ containers. The Contractor
shall ensure the workers place the waste in the appropriate containers.
|
|
Chemical wastes are stored, handled
and disposed of in accordance with the Code of Practice on the Packaging,
Handling and Storage of Chemical Wastes, published by the EPD.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to rectify the problems immediately. Warning shall be
given to the Contractor if corrective actions are not taken within 24 hrs and the Waste Control Group of the EPD shall be
identified.
|
|
Demolition material/waste in dump
trucks are properly covered before leaving
the site.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall
instruct the Contractor to comply. The Contractor shall prevent trucks shall
leaving the site until the waste are properly covered.
|
|
Wastes are disposal of at licensed
sites.
|
Throughout the works
|
Weekly
|
Inform the ER of the noncompliance. The ER shall warn
the Contractor and instruct the Contractor to ensure the wastes are disposed
of at the licensed sites. Should it involve chemical waste, the Waste Control
Group of EPD shall be notified.
|
�� To facilitate monitoring and control over the site performance on waste
management, the following items should be discussed at internal meeting, such
as SSEC and SSEMC meeting, or other established channels for performance
monitoring:
�� Review the WMP including the quantities and types of C&D materials
generated, reused and disposed of off-site; the amount of fill materials
exported from/imported to the site and quantity of timber used in temporary
works construction, sample as presented in Appendix
C for each
process/ activity.
�� Review the implementation of the Construction Waste Disposal Charging
Scheme, and identify areas for improvement
�� Monitoring the achievement of the WMP to assess its effectiveness
�� Discuss and review on the results of the regular Waste Management
Inspection
�� Review the records on the inspection checklist of the Daily Cleaning
and Weekly Tidying
�� Review incidents of non-compliance and discuss the necessary follow-up
action identified
�� Monitor the follow-up action on defects and deficiencies identified
�� Contracts Manager should ensure the
implementation of Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme for recording the
C&D materials being removed off site. The site procedures for
implementation are as follows:
��
Contracts Manager should, within 21 days
after being awarded the contract, make an application for a billing account
solely in respect of that contract, using the form ��EPD-211 Form 1 -
Application for a Billing Account (Construction Work Contract with Value of $1
million or Above)��
��
Project Manager should assign competent personnel for the arrangement
for disposal of construction wastes
��
Before the construction wastes being removed off site, the dump truck
drivers should inform the delegated personnel for the ��Chit��
��
The delegated personnel should fill in a ��Chit�� for that particular
dump truck, issue the Part B & C of ��Chit�� to the dump truck driver and
retain Part A of the ��Chit�� for record
��
The dump truck driver should present Part B & C of ��Chit�� to
operator of designated waste disposal facilities, including the public filling
facility, public sorting facility and landfill, when using the disposal service
��
If the materials accords with the acceptance
criteria, the facilities operator should give Part B of ��Chit�� and a transaction receipt to the truck driver
after completion of the disposal
��
The truck drivers should give Part B of
��Chit�� and the transaction receipt back to the delegated
personnel for record
��
The delegated personnel should properly record all construction wastes being removed off site and check all
relevant records to ensure no illegal dumping
��
The delegated personnel should update
the status of ��Chits��. Enough number of chits should be available for disposal of construction
waste. If additional ��Chits�� required, the delegated personnel should fill in
the form ��EPD-214 Application for Issuance of Chits for Disposal of
Construction Waste for Existing Account-holder�� and submit it to EPD
��
If the ��Chits�� have been lost/ stolen, Project Manager should report to EPD in writing immediately
��
A monthly notice of demand and construction waste transaction
information of the specific project should be received from EPD. Project Manager should pay the specified prescribed charge within 45 days from the
date of the notice and in the manner specified in the notice
��
Contracts
Manager should regularly review the
monthly notice and counter-check with all relevant disposal records to ensure
that the billing account is solely used for payment any prescribed charge
payable in respect of construction waste generated from his/ her project
��
Training on the site procedures for implementation of charging scheme
should be provided to all site staff, including the supervisory staff, all
truck drivers and those employed by subcontractors.
��
All truck drivers must bear a valid Dumping License.
A Filing System should be developed for the
easy filing and effective retrieval of quality records. The environmental
related records should be filed and indexed as per the filing system that
should permit easy identification and access on a frequent basis.
All records, such as permits, site
inspection checklists & reports, etc., relating to the implementation of
the WMP, should be kept adequately and be properly recorded. The records should include, but not limited,
to the followings:
��
Environmental Permit
��
Training Records
��
Inspection Checklists and Records
��
Records of Trip-tickets system
��
Any other related records